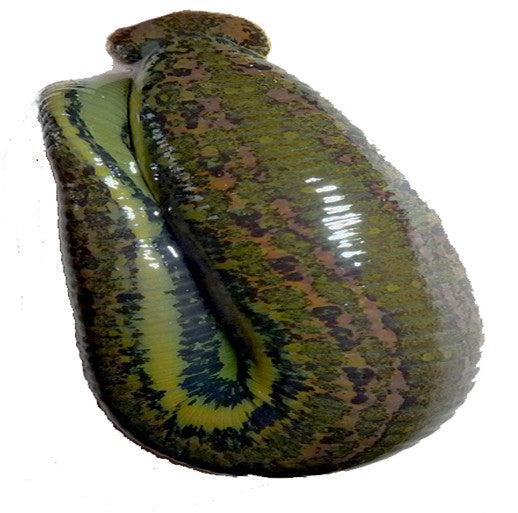
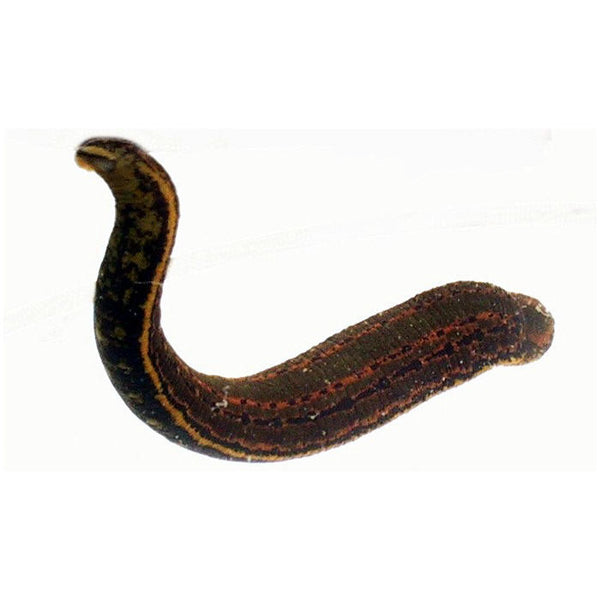
Bloodsucking Turtle Leeches aka
Placobdella parasitica
Found in North America, leech Placobdella parasitica is an excellent parent. Not only can it perform both motherly and fatherly duties simultaneously (it's a hermaphrodite), it also takes good care of its young. These leeches spend most of their lives on turtles, particularly snapping turtles, where they will feed on the blood primarily around the leg pits and tail (where the turtle's formidable jaws can't reach them.) They brood their young on their ventral surface protecting them there until they are big enough to feed on their own, which sometimes means transporting them to their first meal. Despite the caring nature of the leeches post reproduction, the conception of those young is actually quite violent. Leeches will stab small spermatophores into each other in a process known as traumatic insemination.
 UPON ARRIVAL: Immediately transfer your leeches out of the container with special gel and into a jar of cold water!
UPON ARRIVAL: Immediately transfer your leeches out of the container with special gel and into a jar of cold water!
HOW TO GET THEM OUT: Pour out the gel with the leeches from the container. If the leeches are still inside, you may add a bit of cold water and swoosh everything around vigorously. If they are still stuck to the walls, you may try to use your fingers. Regular tweezers may harm the body of the leech, so they are not recommended for use - its best to purchase the recommended leech forceps used for easy removal and handling of the leech. In the absence of forceps, be sure to handle your leeches quickly, so they don’t start sucking blood from your fingers.
BEST CONTAINER TO USE: Keep your leeches in a large glass (or plastic) jar with a tight lid. The container needs to be filled about 1/3 full of ice-cold water. The lid needs to be closed and you may puncture needle-size holes in it. Alternatively, instead of a lid, you may cover your jar with cloth tied with an elastic band.
CARE: Change the leech-water at least once a week. Dump out old water by shaking it around vigorously first, with the lid on, until the leeches’ skins come off (they shed their skins about once a week). Skins appear as slimy whitish-clear particles, floating in the water. Carefully pour-out the old water with skins, taking care not to pour out any of the leeches, then, refill the jar again, close and shake. Repeat this process as many times as needed, until all the skins are completely gone and the water is perfectly clear. Fill the jar again with 1/3 cold water (its ok to use tap) and close the lid tightly.
Keep your jar with leeches in a cold, partly dark place, away from direct sunlight. During winter, they can be kept outdoors, partly-covering the jars with a towel, to protect from full sun-exposure. We do not advise you to feed your leeches during winter. Leech species can keep for 1 year without feeding. Keep your fed leeches apart from the hungry ones, as they will prey on each other. Be sure to purchase separate jars, to separate your fed and hungry leeches properly.